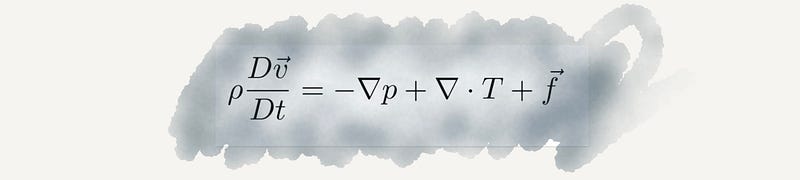Unveiling 17 Equations That Revolutionized Our World
Written on
Chapter 1 Introduction to Pivotal Equations
Mathematician Ian Stewart, a master of prose, delves into the 17 equations that have significantly influenced our world in his book, "In Pursuit of the Unknown: 17 Equations That Changed the World." Stewart presents each equation in an engaging manner, illustrating their profound impact on our daily lives.

Chapter 2 Key Equations and Their Impact
Section 2.1 Pythagorean Theorem
The Pythagorean theorem has played a crucial role in enhancing cartography. It is instrumental in determining the most efficient routes, proving invaluable in fields like architecture and construction.
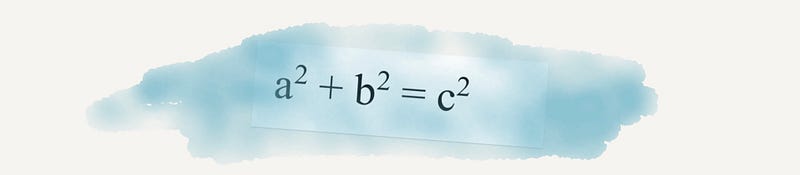
Section 2.2 Logarithms
Logarithms were essential for performing complex calculations long before calculators were invented. Their utility is prominently seen in scientific measurements and various applications, such as assessing sound levels and financial growth.
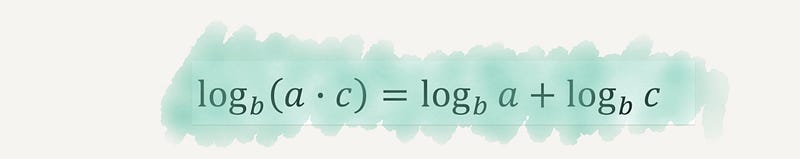
Section 2.3 Calculus
Calculus marks a significant shift from mystical explanations to a more scientific approach. Its applications are ubiquitous in modern technology and science, from analyzing stock market trends to calculating rocket trajectories.
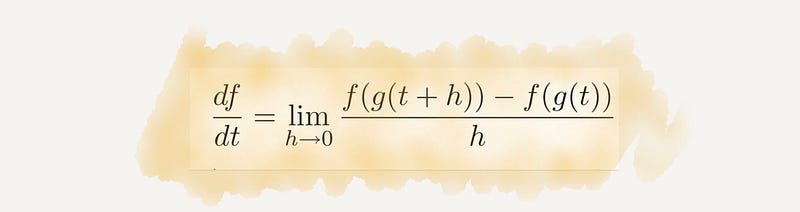
Section 2.4 Newton's Law of Gravity
This law has been pivotal in comprehending celestial movements, providing insights into the dynamics of stars and planets.
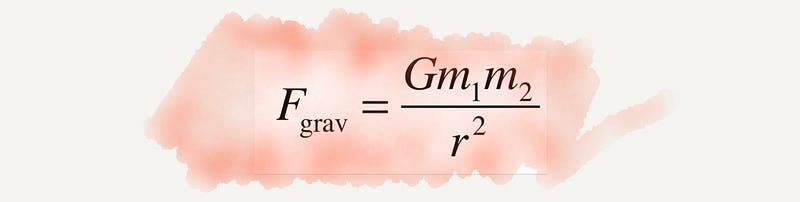
Section 2.5 Complex Numbers
The concept of complex numbers emerged to solve equations with negative roots and is foundational to many modern technologies, including developments in quantum mechanics.
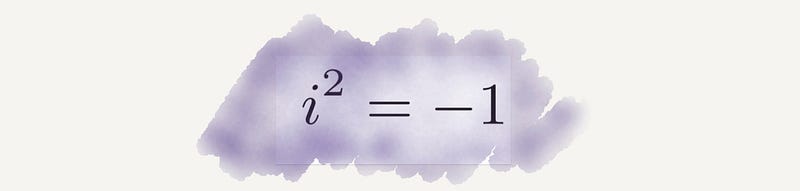
Section 2.6 Euler's Formula for Polyhedra
Euler's formula has crucial applications in aerospace navigation and genetic studies, linking geometry with the intricate structure of DNA.
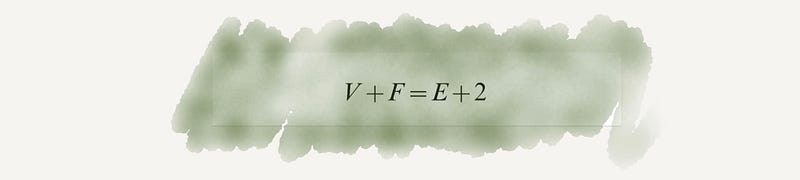
Section 2.7 Normal Distribution
Normal distribution has transformed our understanding of data in various fields, including psychology, education, and medicine, serving as a critical tool for statistical analysis.
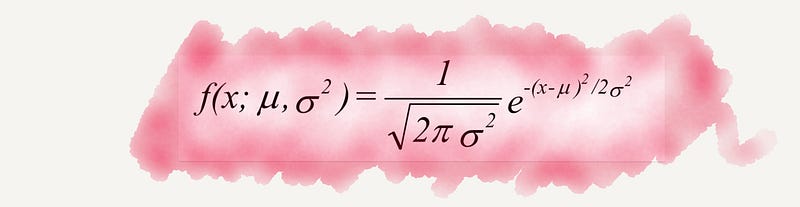
Section 2.8 Wave Equation
This equation is fundamental in understanding the composition of Earth and facilitates the exploration of natural resources like oil. It's also crucial in fields like electromagnetism and fluid dynamics.
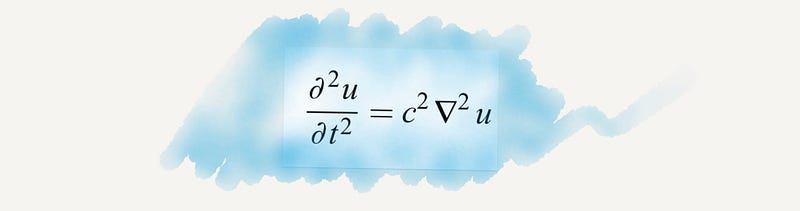
Section 2.9 Fourier Transform
The Fourier transform underpins modern technology, allowing for efficient data compression and signal processing across various digital platforms.
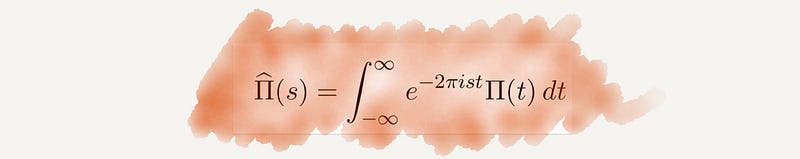
Section 2.11 Maxwell's Equations
Maxwell's equations are the foundation of modern wireless communication, summarizing the principles of electromagnetism.
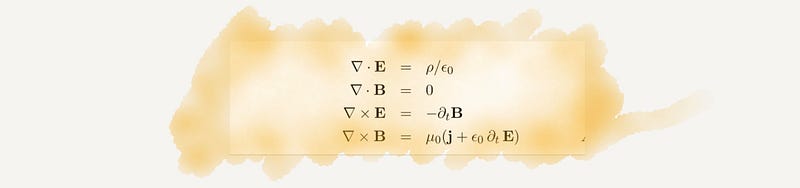
Section 2.12 Second Law of Thermodynamics
This law played a key role during the industrial revolution, establishing the relationship between heat and energy in various systems.
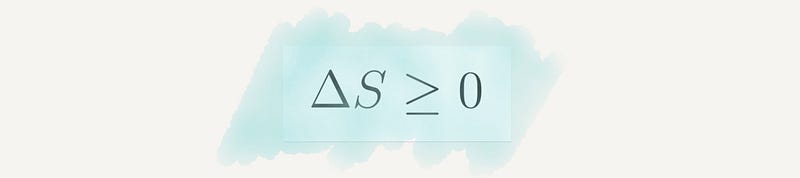
Section 2.13 Relativity
Einstein's theory of relativity revolutionized our understanding of time, space, and gravity, influencing theories related to black holes and the universe's origin.
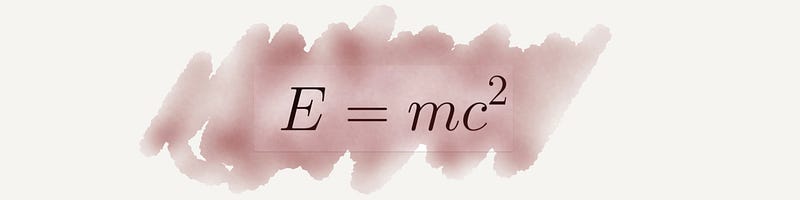
Section 2.14 Schrödinger's Equation
This equation is fundamental in quantum physics, allowing for predictions about particle behavior and facilitating advancements in technology like lasers.
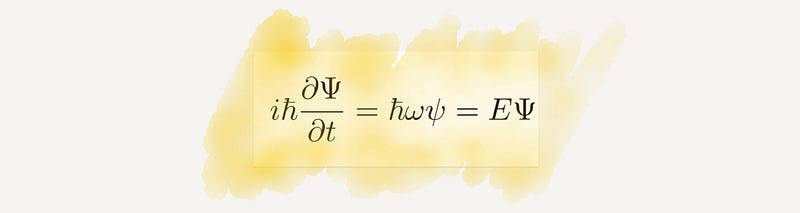
Section 2.15 Information Theory
Information theory models the complexities of communication in the digital age, becoming essential for understanding human-machine interaction.
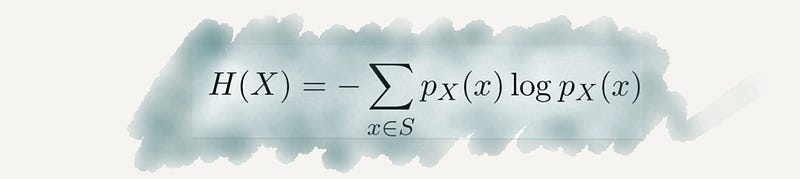
Section 2.16 Chaos Theory
Chaos theory enhances our ability to predict complex systems, notably weather patterns, illustrating how small changes can have significant effects.
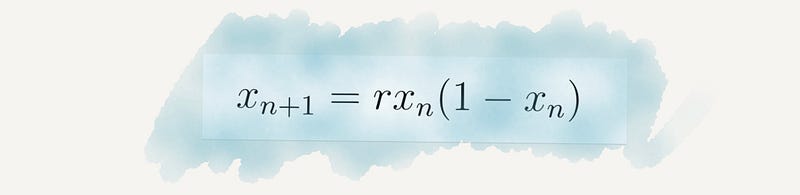
Section 2.17 Black-Scholes Equation
This equation has greatly influenced financial modeling, becoming a topic of discussion in relation to market fluctuations and crises.
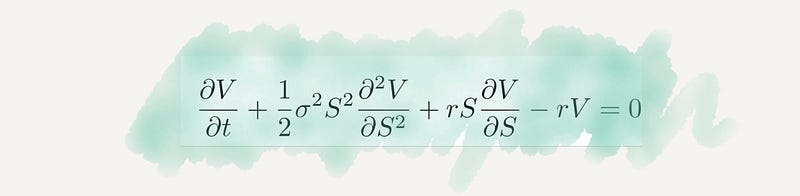
This video explores the pivotal role of the 17 equations that have dramatically altered our understanding of the world.
This video provides an in-depth look at how these 17 equations have fundamentally shaped various fields and technologies.