Exploring the Simulation Hypothesis: Are We Living in a Matrix?
Written on
Chapter 1: Understanding the Simulation Theory
The concept that we might inhabit a simulation rather than a tangible reality has gained traction in recent years. Influential thinkers like Elon Musk suggest that the probability of us not being in a simulation is exceedingly low, estimated at one in a billion. What was once dismissed as mere conspiracy theory is now a topic of serious discourse among scientists and philosophers.
This theory posits that our experiences could be akin to an elaborate hologram, challenging our foundational understanding of reality.
Section 1.1: Historical Roots of Simulation Theory
The notion that our existence might be a simulation is not particularly novel. It echoes ancient philosophies like Plato’s Allegory of the Cave, where individuals are confined to a cave and perceive only shadows on a wall, unaware of the true nature of reality.
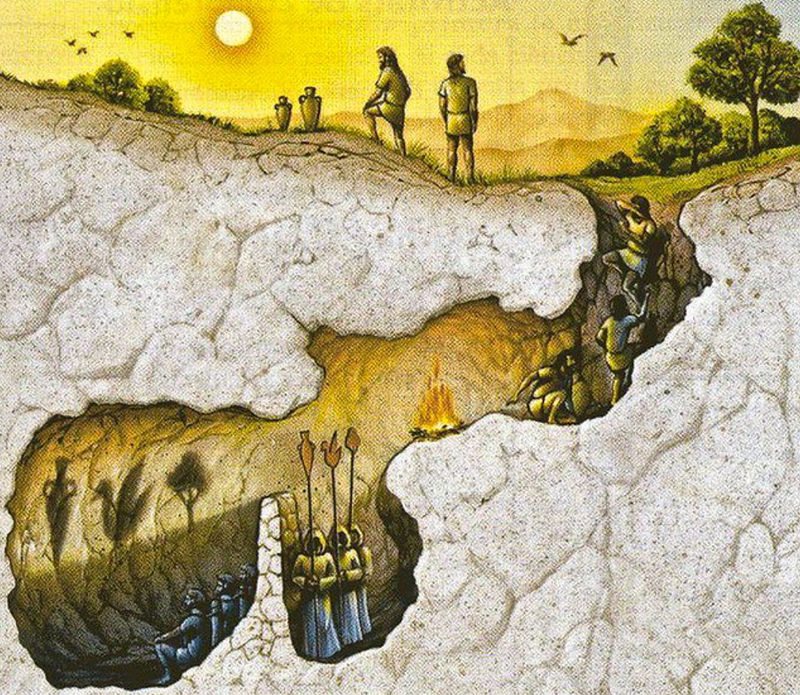

In this allegory, the shadows represent the entirety of their existence, yet the source of these shadows remains elusive. This early philosophical idea parallels contemporary simulation theory, suggesting that our perceived reality may merely be a facade of a more profound truth.
Section 1.2: Philosophical Foundations
The interplay of religion and philosophy has also attempted to explain the concept of a constructed reality. Some belief systems propose the existence of a supreme being who has crafted our universe. Similarly, René Descartes questioned the reliability of our senses, suggesting the possibility of an evil entity deceiving us into perceiving illusions.
In 2003, philosopher Nick Bostrom articulated the modern simulation theory, proposing that one of three scenarios must hold true: humanity may go extinct before achieving the capability to simulate reality, advanced civilizations might choose not to create such simulations, or we are currently living within one.
Chapter 2: The Universe as a Code
The universe operates under strict mathematical laws, from subatomic particles to cosmic structures like black holes. For instance, Planck’s constant governs quantum phenomena, while the speed of light represents the universe's ultimate velocity limit.

This exactitude prompts the question: could these constants resemble computer code that regulates our physical and psychological environments?
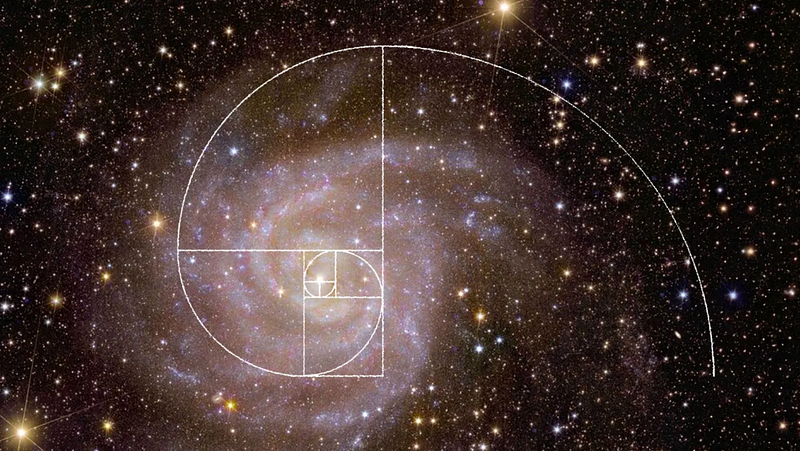
One fascinating aspect of nature is the ubiquitous presence of the Fibonacci sequence and the Golden Ratio. The Fibonacci sequence, where each number is the sum of the two preceding ones, appears in various natural phenomena, including plant growth patterns and shell spirals.
The Golden Ratio, approximately 1.618, is also frequently observed in the measurements of galaxies and even DNA structures. Such recurring patterns hint at a preprogrammed existence rather than mere evolution.
Adding to this notion, physicist James Gates discovered error-correcting codes within the mathematical equations of string theory. These codes, akin to those in computer software for detecting errors, suggest that the universe operates under systems designed to maintain stability, reinforcing the simulation hypothesis.

Section 2.1: Quantum Mechanics and Perception
The double-slit experiment exemplifies peculiar quantum behavior that challenges our understanding of reality. In this experiment, shooting electrons through two slits produces an interference pattern indicative of wave-like behavior. However, if observed, the electrons behave differently, suggesting that reality may not be concrete until it is observed.
Another perplexing concept is quantum entanglement, where two particles remain interconnected regardless of distance. This phenomenon defies classical physics and raises the possibility that reality might be a simulation where entangled particles interact through simulation code rather than physical laws.
Chapter 3: Glitches in the Matrix
The Mandela Effect describes a phenomenon where large groups of people remember events differently than recorded history. A notable example involves the spelling of the "Berenstain Bears," with many recalling it as "Berenstein." Such discrepancies have prompted speculation about glitches in our perceived reality.
Another intriguing occurrence is déjà vu, the sensation of having experienced a moment before. Some theorists propose that déjà vu might signify a reset in the simulation, allowing brief glimpses into alternate timelines.
The science fiction writer Philip K. Dick even suggested that déjà vu could indicate subtle shifts in the simulation. This idea aligns with the notion that our reality may be a sophisticated simulation, occasionally experiencing minor errors or resets.
Unexplained phenomena such as UFO sightings and paranormal events might also hint at glitches within the simulation. UFOs, which often appear to contravene physical laws, may represent instances where the simulation's rules are temporarily bypassed. Similarly, ghost sightings could signify moments when external forces disrupt our programmed reality.
Ultimately, the proposition that we live in a simulation invites profound questions about the essence of our world. Whether or not we are ensconced in an artificial construct, this theory encourages us to explore the complexities of existence from philosophical to quantum perspectives.
The second video provides further insights into the evidence supporting the simulation hypothesis.