Revolutionizing Nuclear Power: A Sustainable Future Ahead
Written on
The Promise of Nuclear Energy
Nuclear energy stands out as a remarkable solution in our quest for sustainable power. It boasts carbon neutrality and an impressively low mortality rate per terawatt-hour (TWh), even lower than that of wind and solar energy, despite accounting for nuclear disasters. Its compact size and minimal environmental impact make it a unique contender among carbon-neutral energy sources. However, one major concern has been the issue of nuclear waste, which has instilled fear in governments and communities globally. Fortunately, Deep Isolation is pioneering technology that promises to address this nuclear waste challenge. What innovations does this technology bring, and could it revitalize the nuclear industry?
While it's essential to acknowledge that nuclear disasters and waste present risks, these dangers are significantly less than those associated with fossil fuels. For instance, a coal power plant generates 100 times more nuclear waste than a single nuclear facility due to the radioactive elements found in coal.

Coal power generates more radioactive material than nuclear.
Examining the Risks
In terms of radioactive waste, coal plants contribute far more to environmental pollution than all nuclear energy combined, including nuclear disasters (excluding nuclear weaponry). While it's critical to have safeguards against nuclear incidents, they do not define the true risks of nuclear energy.
You might raise the question, “But what about nuclear waste?” Yes, there have been fatalities linked to nuclear waste incidents, but these occurrences are extremely rare and isolated to disposal sites. In fact, data on deaths per TWh indicates that more individuals die from accidents related to solar panel installation than from nuclear waste incidents.
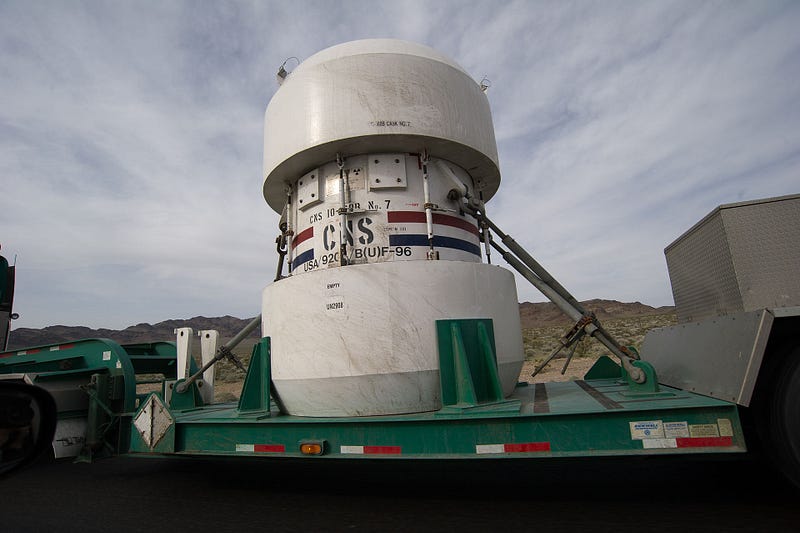

High-grade nuclear waste cask awaiting disposal.
Ultimately, living near a nuclear power plant or waste storage facility poses less risk than residing near a coal plant. Moreover, nuclear energy has a carbon footprint comparable to wind and solar but without the ecological drawbacks, such as extensive land use or massive battery requirements.
Despite its relative safety, the challenge of nuclear waste remains. The small quantities of highly radioactive waste produced can remain hazardous for hundreds of thousands of years. While most nuclear waste loses its radioactivity after several years, a minuscule fraction can emit significant radiation for up to a million years, causing public fear and hindering the expansion of nuclear power plants.

Public concern surrounding nuclear waste storage continues.
Innovative Solutions to Nuclear Waste
This unresolved issue prevents the broader adoption of nuclear energy, despite its potential to significantly reduce carbon emissions. Presently, there are around 250,000 tonnes of nuclear waste worldwide, and various proposed solutions—ranging from space disposal to underwater storage—have not withstood scrutiny. However, Deep Isolation offers a promising alternative.
By leveraging advancements from the fossil fuel sector, Deep Isolation has developed a cutting-edge nuclear waste disposal method. Let’s delve deeper into their approach.
Current practices avoid burying high-grade nuclear waste due to the slim risk of contamination of water supplies. Even geological activity could lead to potential leaks. However, the fossil fuel industry has perfected deep drilling and geological surveying techniques to extract every last drop of oil.
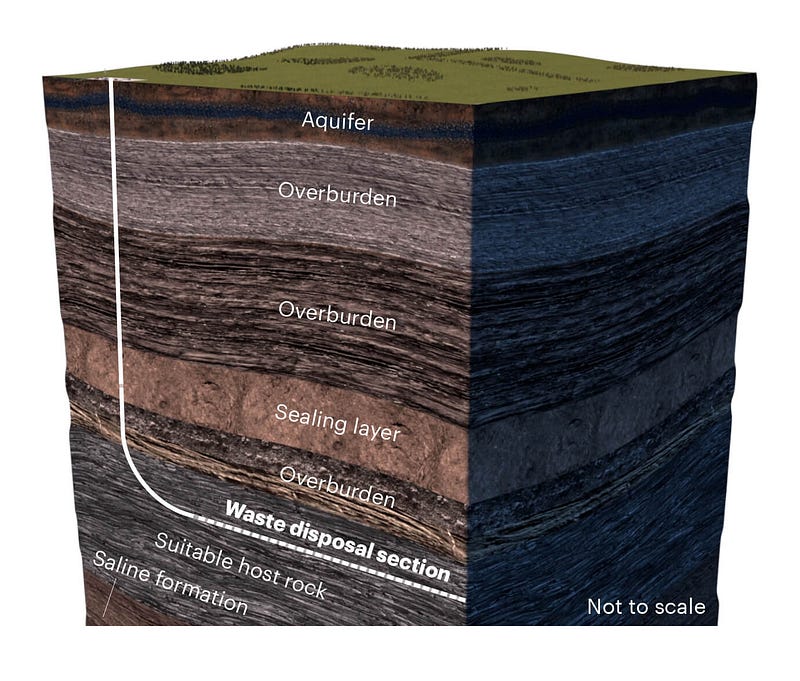
Deep Isolation's innovative waste disposal plan.
Deep Isolation aims to utilize these technologies to create boreholes deep beneath the water table, targeting stable rock formations that will remain undisturbed for billions of years. At great depths, they plan to drill horizontal sections to securely store high-grade nuclear waste, subsequently sealing the site with concrete. The immense pressure from the surrounding rock effectively isolates the waste from the surface.
This video discusses Deep Isolation's innovative waste management technology.
Additionally, the nuclear waste will be encased in solid, durable rods to prevent leaks. Even in the unlikely event of a breach, the waste cannot escape to the biosphere due to the thousands of feet of rock shielding it from the surface.
Importantly, this method allows on-site storage, eliminating the need for transportation of high-grade nuclear waste, which could enhance safety and reduce operational costs.
Deep Isolation has already developed prototypes to demonstrate the viability of their approach and has recently received a $3.6 million grant from the U.S. Department of Energy to create a universal nuclear waste disposal solution applicable to all nuclear reactors.
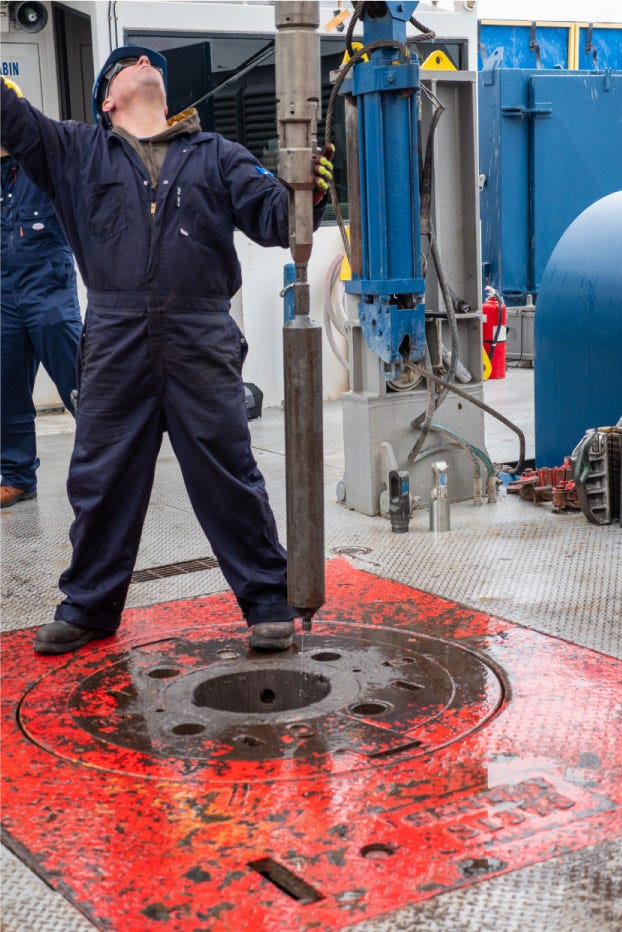

Demonstrating the lowering of a nuclear waste casing into a borehole.
As this technology matures and becomes available globally, it will address one of the most significant obstacles to nuclear energy expansion. With the advent of commercial molten salt reactors—expected to be more efficient and cost-effective—the resurgence of nuclear power appears promising.
By employing technology originally designed for oil extraction, we can tackle one of the most pressing issues associated with nuclear energy. With Deep Isolation's solutions, nuclear power could play a central role in mitigating climate change. The prospect of a nuclear revolution is on the horizon, and we must act swiftly to embrace this opportunity.