The Future of Data Engineering: Is Zero ETL the Game Changer?
Written on
Chapter 1: Understanding Zero ETL
In today's tech landscape, new SaaS cloud-based solutions are transforming the way we handle data. Imagine IT services and data lakes functioning as effortlessly as flipping a switch. But does this mean that data engineers could become obsolete?
Picture a scenario where there are no more frustrated IT personnel or data engineers who are burdened with constructing complex data pipelines. Instead, data scientists could seamlessly integrate data themselves using a zero ETL approach, merely by dragging and dropping, thus making the data actionable and insightful. This concept is undoubtedly appealing to every CIO, but how dependable is this model?

Section 1.1: The Mechanics of Zero ETL
First, let's delve into the technology behind this approach. What does Zero ETL entail? Essentially, it refers to the capability of modern cloud-based data warehouses or lakehouses that leverage services from major cloud providers to analyze data directly from various sources. Rather than extracting data from SQL or NoSQL databases, transforming it, and storing it in a data lake or warehouse, one can directly query the data (often through SQL). The benefits of this approach include:
- Elimination of the need for data pipelines, especially if they were previously developed.
- Reduction of redundant data storage, which is both costly and impacts performance.
- Ensured up-to-date data availability.
One notable example in this realm is Google BigLake, which allows access to multiple data sources across platforms like Azure and AWS for SQL-based analysis. While these advantages are compelling, one might wonder, what’s the catch?
The first video, The Zero-ETL Approach: Enhancing Data Agility and Insight, explores how this method can revolutionize data handling.
Section 1.2: Potential Pitfalls of Zero ETL
However, there are concerns. Critics argue that such an approach may lead to data chaos, where a data lakehouse could devolve into a data swamp. This risk arises when data is scattered and analyzed solely by end-users, which can create inconsistencies.
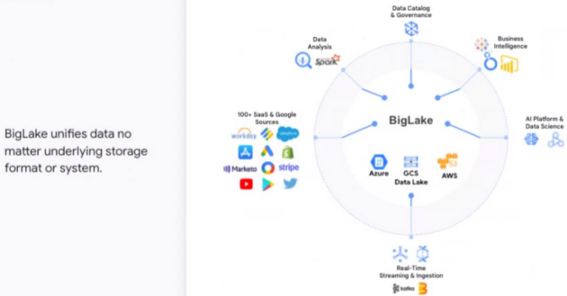
Google BigLake serves as a solution to this potential chaos. With services like DataPlex, organizations can assign access rights to external data sources, create view logic, and integrate data into a catalog. This fosters a secure data governance framework, enabling a robust data mesh. Other major cloud platforms such as AWS and Azure offer similar functionalities.
Chapter 2: The Evolving Role of Data Engineers
The emergence of Zero ETL is undoubtedly simplifying data integration. With fewer services, less duplicate data storage, and reduced custom programming, some tasks traditionally handled by data engineers are now being streamlined. However, challenges persist. Companies without cloud operations will not benefit from these advancements since such architectures are primarily cloud-based.
The second video, Fastest way to Start Your Data Engineer Journey in 2024, discusses how aspiring data engineers can navigate this evolving landscape.
Despite this shift, organizations leveraging cloud services will still require data engineers. Certain systems remain complex and not easily integrated. The roles of data engineers may evolve from building ETL pipelines to utilizing more integrative services, focusing on data governance, data mesh implementation, and fostering a data culture within the organization. For those interested in understanding the importance of data culture, further exploration is encouraged.
What is Data Culture?
In conclusion, while the Zero ETL approach presents significant opportunities, it also introduces new complexities and responsibilities for data engineers. Understanding and adapting to these changes is essential for future success in the data landscape.
Sources and Further Readings
[1] THENEXTPLATFORM (2022)