Exploring the Role of Dopamine in Consciousness and Awareness
Written on
Chapter 1: Understanding Consciousness
Consciousness remains one of the most intricate and vital subjects in science. While we all experience consciousness as a form of self-awareness and interaction with our environment, pinpointing the specific brain areas responsible for this subjective experience poses a significant challenge. This enigma is often referred to as the "hard" problem of consciousness.
As of now, even the simpler aspects of brain mechanisms that contribute to conscious experience in both animals and humans are still not fully understood. Many individuals face consciousness disorders following severe brain injuries, which can lead to states like vegetative conditions—where a person appears awake but lacks any sign of awareness—or comas. Similar temporary lapses in awareness can occur during anesthesia or psychedelic experiences. Thus, gaining a clearer understanding of consciousness is crucial for clinical applications.

Image credit: neurosciencenews.com
Section 1.1: The Default Mode Network
Recent advancements in functional neuroimaging have enabled scientists to map brain activity and identify regions associated with consciousness. One notable discovery is the involvement of the default mode network (DMN) in self-awareness, which appears to be integral to the concept of the ego.
Research has shown a significant relationship between reduced connectivity in the DMN and experiences of "ego dissolution" under psychedelics—where individuals report a temporary loss of self-identity. Furthermore, people with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) exhibit decreased DMN activity, while those suffering from depression and anxiety demonstrate heightened DMN activity. Notably, damage to this network can lead to consciousness disorders and is also impacted by anesthesia.
Subsection 1.1.1: The Enigma of Unconsciousness
Sometimes, patients may seem unresponsive but are, in fact, conscious. In a remarkable 2006 study, researchers found that a 23-year-old woman, believed to be in a vegetative state due to severe brain trauma, exhibited signs of awareness. When asked to visualize playing tennis, her brain scans revealed activity in motor regions, and similar responses were seen when she imagined navigating her home.
These findings highlight that while traditional clinical assessments may fail to detect awareness, brain imaging can uncover hidden consciousness. Other studies suggest that approximately 20% of patients in vegetative states may be conscious yet unable to communicate, emphasizing the need for better diagnostic methods.
Chapter 2: The Role of Dopamine in Consciousness
The quest to aid individuals with consciousness disorders necessitates an understanding of how various brain regions communicate. Among the neuromodulators that facilitate this communication, dopamine stands out. Known for its association with reward, dopamine also plays a critical role in directing our focus outward and motivating action.
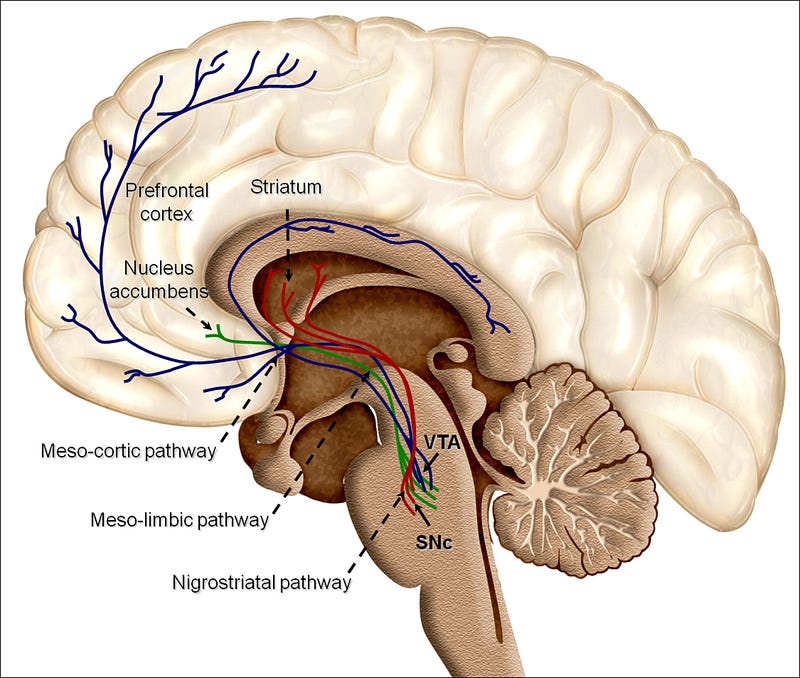
Dopamine is released from the ventral tegmental area (VTA) and influences many cortical areas, including those related to consciousness disorders. Research indicates that dopamine release is compromised in minimally conscious individuals, while some studies suggest that administering dopamine-targeting medications can enhance consciousness.
A recent study published in the Proceedings of the National Academies of Sciences has established a link between conscious brain activity and dopamine levels. The research found that impaired VTA function correlates with consciousness disorders, indicating that restoring VTA activity may be crucial for recovery. Moreover, the dysfunction in dopamine is associated with problems in the DMN, underscoring its importance for self-awareness.
In the first video, "Leverage Dopamine to Overcome Procrastination & Optimize Effort" from Huberman Lab, the discussion revolves around how dopamine influences motivation and behavior. This insight can be particularly relevant in understanding its role in consciousness and awareness.
The second video, "#1 Neuroscientist: Truth About Laziness, Discipline, Exercise, Stress & Journaling" featuring Andrew Huberman, explores the neuroscience behind common human behaviors and their connection to dopamine, providing further context to its influence on our consciousness.
Conclusion
The investigation into consciousness is a field marked by profound scientific intrigue and complexity. Although a comprehensive understanding may remain elusive for some time, recent findings underscore dopamine's vital role in elucidating the origins of consciousness. This research not only advances our knowledge but also offers promising avenues for developing treatments for consciousness disorders through dopamine-targeting medications.
Thank you for your interest in science! We welcome your questions, comments, and suggestions for future articles below. While you're here, consider exploring some of our other pieces.
DMT: The Spirit Molecule That Keeps Amazing Us
Research suggests that this powerful psychoactive chemical could be produced within our brains.
Ibogaine: A Promising Psychedelic Therapy For Drug Addiction
Research suggests ibogaine therapy can eliminate withdrawal symptoms and cravings towards drugs in struggling addicts.