The Untouched Wilderness of Antarctica: A Fragile Future
Written on
The Enigmatic Continent
Nestled at the southernmost point of the Earth, Antarctica remains one of our planet's most captivating and largely uncharted territories. Although the Antarctic Treaty effectively bans commercial mining activities, the escalating interest in untapped natural resources is beginning to stir concerns about the preservation of this icy expanse.
The Geological Legacy of Antarctica
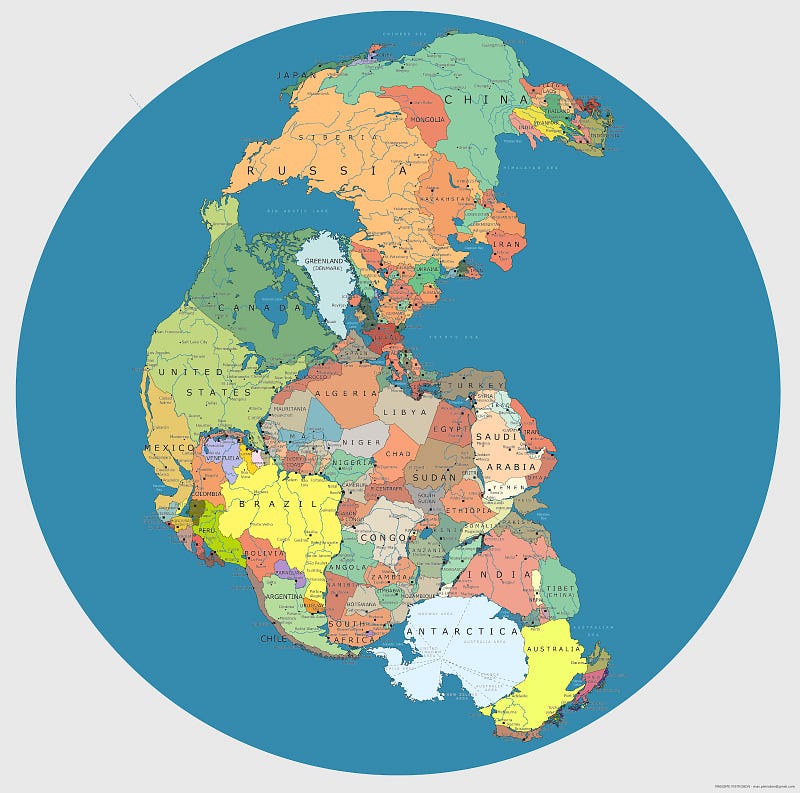
Antarctica spans approximately 14 million square kilometers, ranking as the fifth-largest continent. Millions of years ago, during the era of Pangaea, this landmass was connected to what are now Africa, South America, India, and Australia. At that time, the continent enjoyed a much warmer and wetter climate, fostering rich biodiversity, including lush forests.
As tectonic activity caused Pangaea to fracture, Antarctica gradually drifted southward, distancing itself from the other continents. This migration led to a colder climate and ultimately resulted in the formation of its vast ice sheets. The sedimentary layers present in Antarctica today, which are rich in fossils and coal deposits, offer a glimpse into its ancient, more temperate past.
The geological history suggests that Antarctica could be hiding significant natural resources, similar to those found on other continents that were once part of this unified landmass. Thus, it stands to reason that if certain minerals are located in nearby continents, analogous resources may lie beneath the Antarctic ice.
Is Antarctica a Resource-Rich Continent?

With a resident population that fluctuates between 1,000 to 5,000 individuals, the continent's ice can reach a staggering thickness of 4.7 kilometers. The potential for resource exploitation in Antarctica is garnering increasing attention, yet it encounters major hurdles, primarily the thick ice cover that complicates both exploration and extraction efforts.
While geological theories indicate the presence of minerals and hydrocarbons, the challenge lies in locating and accessing these resources buried beneath the ice. Current mining technologies would require significant adaptation to suit the extreme conditions unique to Antarctica, which are vastly different from the more accessible environments typically associated with mining and oil extraction.
A parallel can be drawn with the evolution of offshore oil drilling. Initially, extraction was confined to shallow waters where it was economically viable. As coastal resources dwindled and global demand surged, advancements in technology allowed the industry to venture into deeper, more challenging waters. This evolution illustrates that necessity can drive innovation, especially when financial incentives are substantial.
However, the Antarctic Treaty currently imposes stringent limitations on any commercial exploitation. Let's delve into the reasons behind this.
The Restrictions of the Antarctic Treaty

Home to around 90% of the world's ice and 70% of its fresh water, Antarctica's vast resources come with significant environmental responsibilities. Large-scale resource exploitation could have dire consequences, including:
Environmental Impacts
Antarctica's ecosystem is delicate and unique. Intensive extraction activities could disrupt local wildlife and accelerate the melting of the ice cap, further contributing to climate change. The risk of pollution, such as oil spills and contamination from mining waste, poses a severe threat to both land and marine environments.
Scientific Consequences
Resource extraction would interfere with crucial scientific research that helps us understand global climate dynamics. Large-scale human activities could obliterate unique sites of scientific significance, including vital climate records preserved in the ice.
Geopolitical Consequences
The pursuit of resources could intensify territorial disputes in Antarctica, which are currently on hold due to the Antarctic Treaty, potentially leading to international tensions. Moreover, the continent is one of the last untouched wilderness areas, raising ethical concerns about the impact of exploitation on future generations.
Final Thoughts
Antarctica, a continent enveloped in ice and intrigue, harbors potential resources beneath its frozen exterior. Despite theories suggesting the existence of valuable minerals and hydrocarbons, the continent's extreme conditions present formidable barriers to exploration and extraction.
The Antarctic Treaty emphasizes environmental preservation and scientific inquiry, reflecting a global consensus on protecting this unique ecosystem. While future technological advancements may make resource extraction more feasible, ethical implications, environmental risks, and geopolitical factors make the issue highly contentious.
Thank you for engaging with this exploration of Antarctica's delicate balance. I look forward to sharing more insights in future articles.