Unlocking Metabolic Health: Insights from a Glucose Monitor
Written on
Chapter 1: Introduction to Blood Glucose Monitoring
In recent times, I’ve developed a keen interest in enhancing my health, which may be attributed to various factors, including reaching my 30s and facing health challenges both personally and within my family. This journey has prompted me to delve deeper into health management and experiment with strategies that might lead to a healthier lifestyle.
A significant part of my exploration involved using a continuous blood glucose monitor developed by Levels. This device tracks blood sugar levels continuously and syncs data to an app, allowing for real-time insights into my metabolic health.
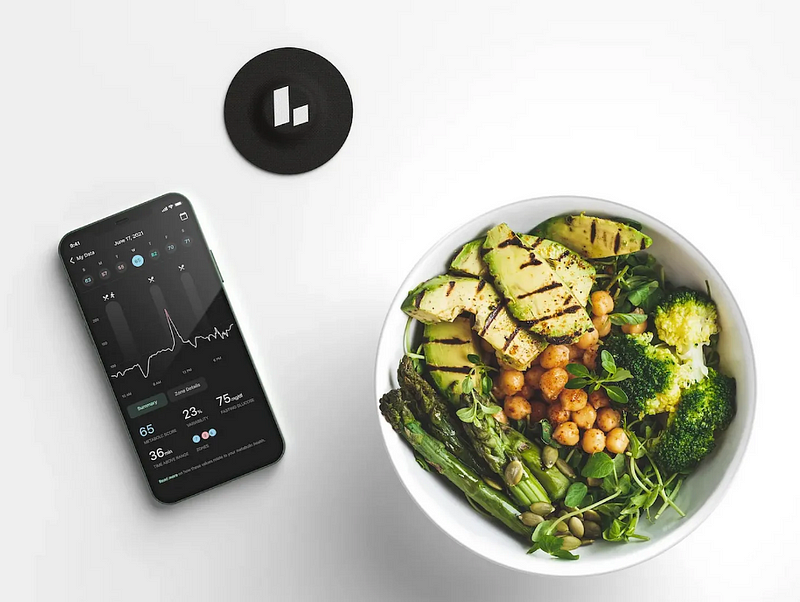

Chapter 2: Understanding Glucose Monitoring
This monitoring system not only reveals how well your body manages glucose spikes but also identifies which meals lead to these spikes. It provides a less invasive alternative to traditional finger-prick methods often used by diabetes patients. Despite the initial investment of $199 for an annual membership and an additional $199 for a month’s supply of monitors, I found the expense justified in the pursuit of better health.
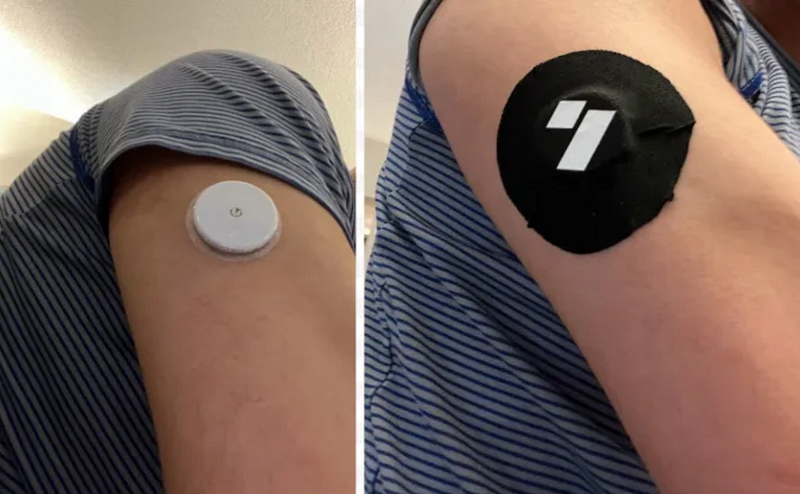
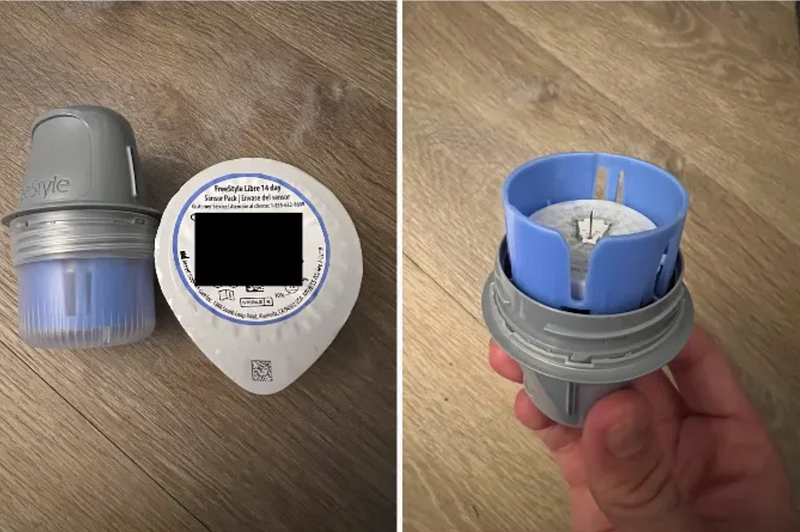
After a week, my supply kit arrived, containing two monitors, alcohol wipes, and a Levels sticker patch. The application process was surprisingly painless, involving a simple press of the applicator to my arm. Every eight hours, I scanned the monitor using my phone to upload the data, with a replacement needed every 14 days.

Section 2.1: The Importance of Monitoring Blood Sugar
Keeping track of blood glucose levels is crucial since how effectively your body processes glucose impacts overall health. When you consume food, carbohydrates break down into glucose, prompting the pancreas to release insulin, which facilitates glucose absorption into cells. The cells then convert glucose into ATP, the energy source for cellular functions.

The efficiency of this process indicates your metabolic health. Poor glucose metabolism can lead to various health issues, including diabetes, highlighting the necessity of managing glucose levels to prevent excessive strain on the pancreas.

Section 2.2: Key Learnings from My Experience
One key takeaway from my experience with the glucose monitor was the significance of meal timing in relation to exercise. Engaging in physical activity naturally lowers blood glucose levels, making it beneficial to exercise after meals. This practice aligns with common advice to take short walks post-meal.
Interestingly, I observed that many individuals at the Costco food court tend to eat before shopping, which may not be the optimal order. Eating first and then walking around the store can help manage blood sugar levels more effectively than eating and then sitting in the car.
I also noted that blood glucose levels stabilize during sleep, reinforcing the need to avoid late-night eating, which can disrupt metabolic processes.
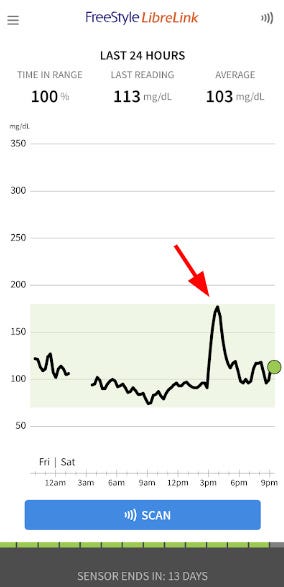
Section 2.3: Meal Portions and Their Impact
Further insights revealed that consuming large meals in one sitting can lead to significant spikes in blood glucose levels. Conversely, spreading the same amount of food across smaller meals results in more manageable glucose levels.
This experience reminded me to practice moderation in eating habits, reinforcing the idea that it’s acceptable to stop when feeling about 70% full and save the rest for later.
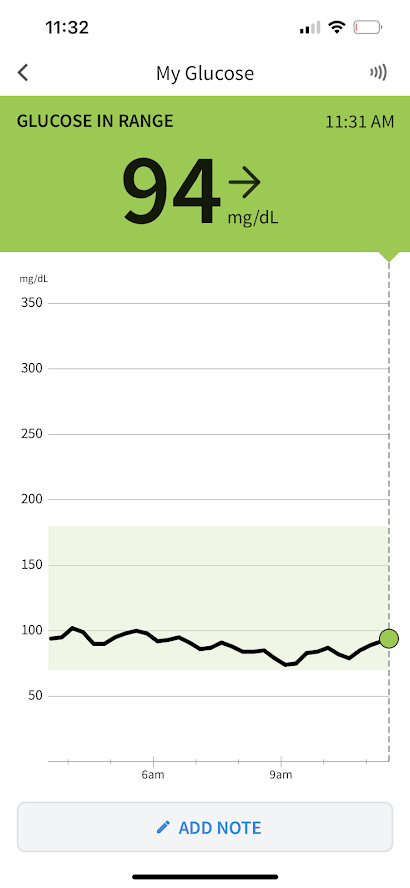
Final Thoughts on Blood Glucose Monitoring
Using the blood glucose monitor has transformed the way I approach health decisions, prompting me to consider how my choices affect my blood sugar levels. Beyond simply avoiding high-carb foods, I’ve become more mindful of my daily routines.
For instance, I now prioritize physical activity after meals and ensure I eat a small snack before workouts to maintain energy levels, knowing that my glucose may dip during exercise.
While the insights gained from this experience are widely known, the practical application of these strategies can significantly enhance one’s metabolic health. Here are some actionable tips to help manage blood glucose levels:
- Take 15-20 minute walks after meals
- Snack before and after workouts
- Break large meals into smaller portions throughout the day
- Avoid eating 2-3 hours before bedtime
- Limit high-carb foods
If you're interested in exploring Levels glucose monitors, you can find more information through the provided link.

Chapter 3: Video Insights on Blood Sugar Tracking
This video discusses personal insights from wearing a continuous glucose monitor, highlighting the significance of blood sugar management.
In this video, the speaker shares valuable lessons learned from tracking blood sugar levels, emphasizing the importance of monitoring for better health decisions.