Exploring the Unique Vision of Various Animals
Written on
Chapter 1: Understanding Animal Vision
Animals, including your beloved pets, often exhibit partial colorblindness, yet their vision can surpass human capabilities in various ways. The way different species perceive their environment is intricately tied to their ocular physiology. Humans possess three types of cone cells, enabling us to perceive red, green, and blue light—this classification makes us trichromats. In contrast, many animals have fewer or more types of photoreceptors, affecting their visual experience. For instance, some creatures have only two types of cones, rendering them partially colorblind, while others possess four types, allowing them to see ultraviolet light. Additionally, certain species can detect polarized light, which consists of light waves oscillating in a singular plane.
“Imagining what another animal perceives can be tempting,” remarks Thomas Cronin, a visual physiology professor at the University of Maryland. However, while speculating on animal cognition may be fanciful, gaining insight into their visual perspective is within reach.
The left images below illustrate how various animals view the world, while the right images depict human vision.
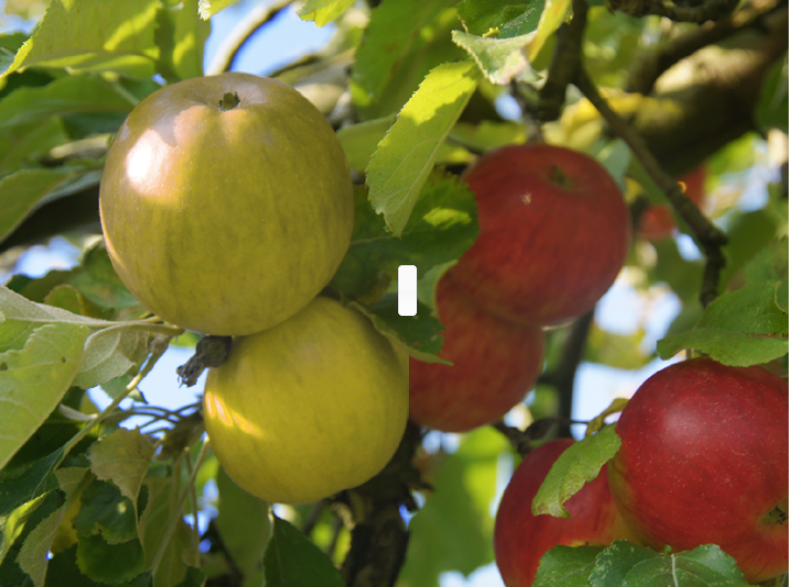

Cat Vision
According to Dan-Eric Nilsson, a zoologist at the University of Lund, the visual experience of a cat remains elusive. However, we can approximate it. Cats are dichromats, possessing only two types of cones, similar to humans with red-green colorblindness. This means their perception combines red and green hues into one indistinguishable color.
While cats have a lower visual acuity than humans, resulting in a somewhat blurrier image, they excel in low-light conditions due to a higher rod count. In daylight, their vision is approximately six times less sharp than that of humans, though this is not illustrated in the accompanying image.
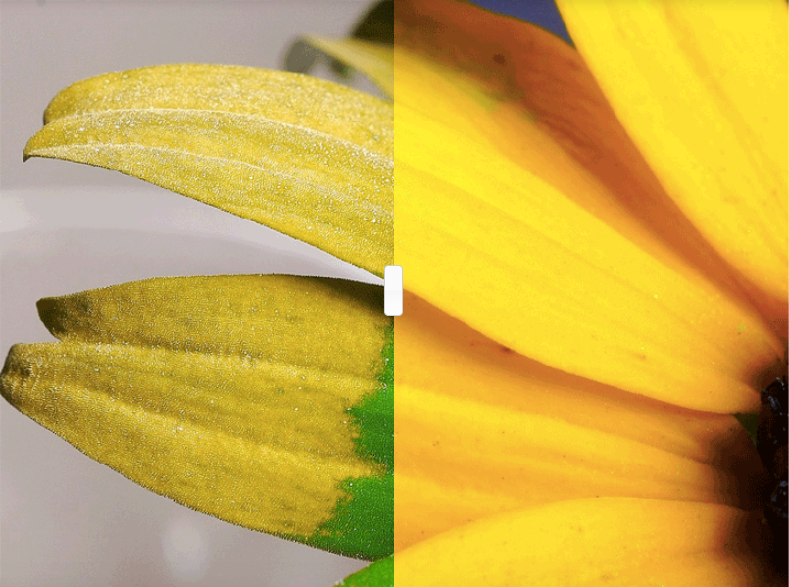

Bee Vision
Similar to humans, bees are trichromats, but their photoreceptors respond to yellow, blue, and ultraviolet light instead. This ability allows them to detect patterns on flowers that signal the presence of nectar. Nilsson notes that bees can perceive multiple shades of ultraviolet light.
Bees' compound eyes consist of thousands of tiny lenses, creating a soccer-ball-like structure. Each lens provides a singular "pixel" in their vision, which results in low-resolution but broad visual perception. If humans had compound eyes as effective as bees', they would need to be as large as hula hoops to match our visual clarity.
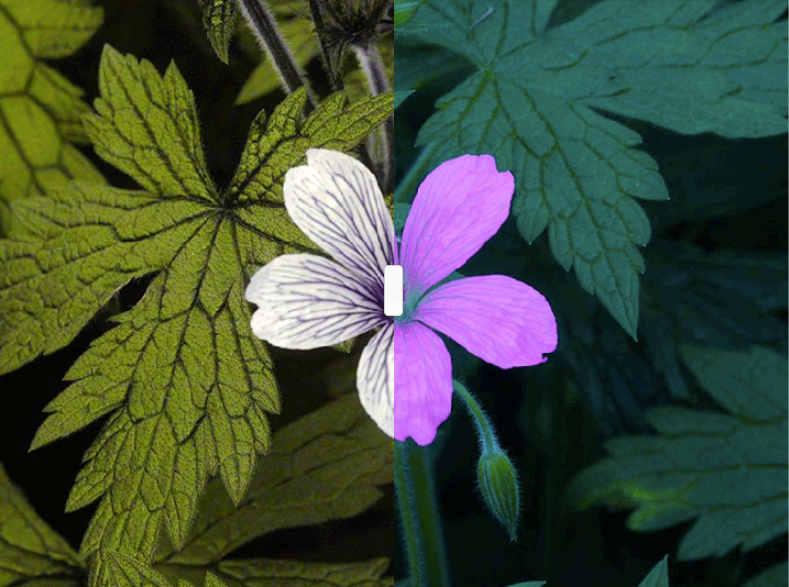

Bird Vision
Birds are tetrachromats, possessing four types of cone cells that allow them to see red, green, blue, and ultraviolet light simultaneously. Notably, some birds of prey have vision that is about 2.5 times sharper than humans. If Nilsson could delve into the consciousness of another species, he notes that birds would be fascinating. However, humans are limited; we lack the necessary receptors and brain pathways to comprehend ultraviolet light, although technology like binoculars and UV-converting cameras can help us see what birds perceive.
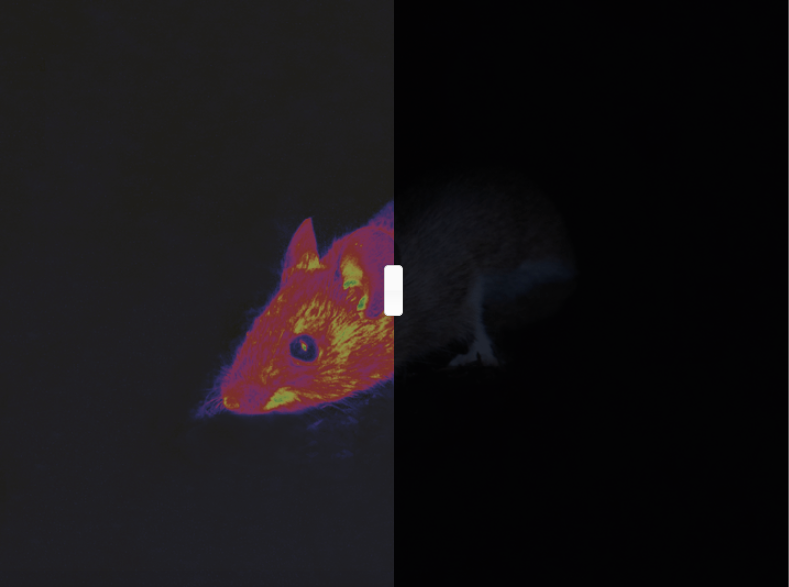
Rattlesnake Vision
Rattlesnakes exhibit low-resolution color vision during the day but have an abundance of rod cells for enhanced nocturnal sight. What distinguishes rattlesnakes is their unique capacity to sense infrared light. They possess pit organs that detect heat, allowing them to perceive the thermal signatures of their prey. David Julius, a physiology professor at the University of California, San Francisco, explains that a specific receptor, TRPA1, in their nerve cells enables this transformation of infrared light into nerve signals. Interestingly, this receptor also triggers pain responses in humans when consuming spicy foods.
Through their brain's integration of visual data and thermal information from their pit organs, rattlesnakes can effectively visualize the warmth of nearby prey, akin to observing through an infrared camera.
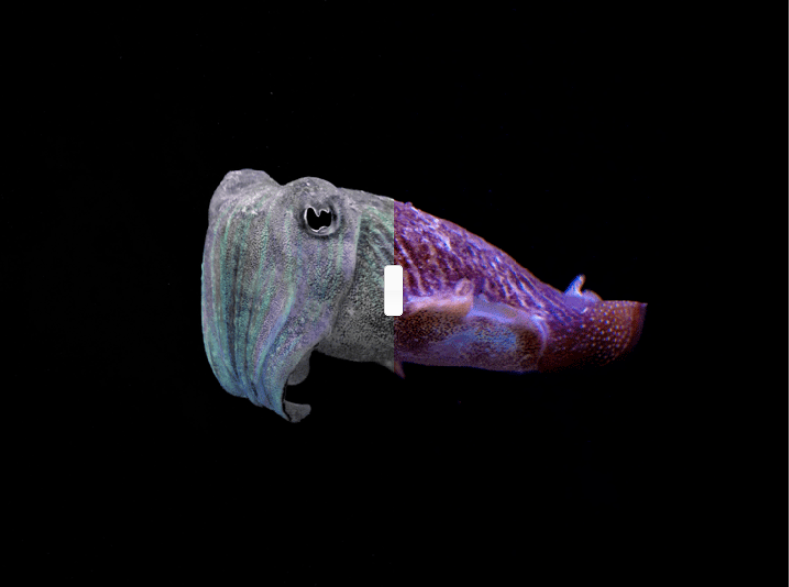

Cuttlefish Vision
The visual experience of cephalopods like cuttlefish diverges significantly from our own due to their distinct evolutionary path. Unlike vertebrates, cephalopods lack a blind spot, and their pupils are uniquely shaped, resembling a W. Despite their remarkable hunting abilities, cuttlefish have blurrier vision than humans, only capable of reading headlines rather than fine print. They possess one type of photoreceptor for detecting shades of gray, and another pair for sensing polarization.
While humans experience polarized light primarily through sunglasses, cephalopods can directly perceive it. Cuttlefish communicate through polarization patterns on their skin, merging the gray shades they see with polarization data, reminiscent of the rattlesnake's infrared capability.
“I believe we can relate to the perceptions of mammals like dogs or monkeys,” Cronin states, “but cephalopods are so evolutionarily distinct that we cannot fathom their experiences. However, imagining it can be intriguing.”
Elizabeth Preston is a former editor of Muse, a science and ideas magazine for youth, and the author of Inkfish, a blog dedicated to science and cephalopods. Follow her on Twitter @Inkfish.
Chapter 2: Visual Insights from Animals
The first video, "HOW ANIMALS SEE THE WORLD," explores the fascinating ways animals perceive their surroundings.
The second video, "How Animals See the World," provides an in-depth look at the visual systems of various species and how they compare to human vision.