Exploring the Surprising Presence of Ice on Mercury
Written on
Chapter 1: The Enigma of Ice on Mercury
The concept of ice on Mercury, the planet closest to the Sun, appears paradoxical at first glance. The intense heat, with surface temperatures soaring up to 400 degrees Celsius (750 Fahrenheit), seems to preclude the presence of ice. However, recent research indicates that these extreme temperatures may actually facilitate the formation of ice on this small planet.
Many scientists theorize that water on Mercury was likely introduced by asteroid impacts. Within the planet's polar craters, ice can remain perpetually frozen in darkness. As David Williams from NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center noted back in 2012, “Water ice on Mercury’s surface is directly exposed to the vacuum of space and can rapidly sublimate unless kept at low temperatures. This suggests that ice can only survive in regions shielded from sunlight, primarily near the poles, where the depths of certain craters provide a permanent shadow.”
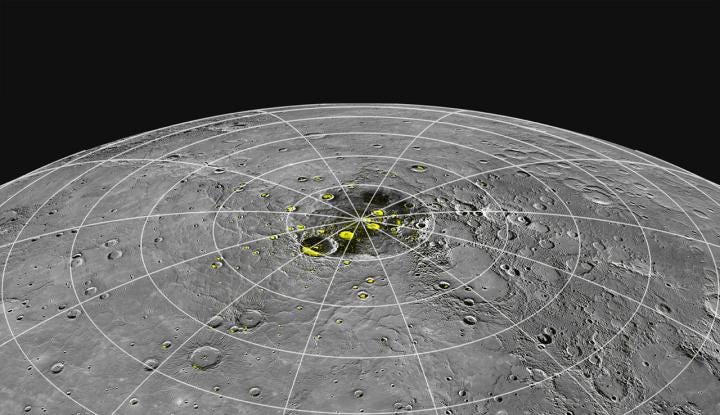
The Messenger spacecraft confirmed the existence of ice in the polar regions of Mercury. Image credit: NASA/Messenger
Section 1.1: The Role of Hydroxyls
Chemical reactions may be crucial in explaining the presence of water ice on Mercury. Central to this process is the solar wind, a stream of charged particles, including protons, that emanates from the Sun.
The minerals on Mercury's surface contain hydroxyl groups, which are made up of one hydrogen atom and one oxygen atom. Most of these molecules are created by protons from the solar wind. The intense heat excites hydroxyl molecules, leading to their release from the surface, resulting in interactions that create water and hydrogen. These molecules then become mobile across Mercury's surface.
Some water molecules may be broken down by sunlight or rise high into the atmosphere, but many settle in the dark recesses of polar craters. Due to Mercury's lack of a significant atmosphere, which would otherwise distribute heat, these shadowy areas allow ice to remain frozen, despite the planet's extreme temperatures.

Thom Orlando (left) and Brant Jones (right) lead a study on ice presence in Mercury. Image credit: GA Tech/Rob Felt
Subsection 1.1.1: Groundbreaking Research
“This idea is not entirely novel; the fundamental chemical mechanisms have been documented many times since the late 1960s. However, applying these mechanisms to the complex surfaces of a planet is pioneering work,” stated Brant Jones from Georgia Tech’s School of Chemistry and Biochemistry. Researchers believe that this process could account for as much as 10% of the ice found on Mercury.
Chapter 2: The Discovery of Water Ice
Evidence of water ice on Mercury was initially detected through radar observations from Earth, which revealed unmistakable signs of this molecule. In 2011, the MESSENGER spacecraft flew by Mercury and confirmed the presence of water ice in the planet's polar craters.
“I would prefer to be Mercury, the smallest of seven [planets] orbiting the Sun, rather than the foremost of five [moons] circling Saturn,” — Johann Wolfgang von Goethe.
Much like the Moon, Mercury is riddled with numerous craters and is slightly smaller than its lunar counterpart. This has led to comparisons of the chemical and geological activities on both celestial bodies. While it is believed that the Moon also contains water ice in its perpetually shadowed polar craters, the properties of this water differ from those found on Mercury. The reasons for these differences remain unclear, but they may stem from the distinct mechanisms through which ice forms in the polar regions of both bodies. The Moon's colder environment does not support the hydroxyl reactions observed on Mercury, although a similar process could occur on our natural satellite.
The magnetic field of Mercury is approximately 10% as strong as Earth's protective magnetic shield. Nevertheless, it is sufficient to guide protons and other charged particles into spirals, delivering them to Mercury's surface.
“These phenomena resemble large magnetic tornadoes, which cause significant proton movements across Mercury’s surface over time,” explains Thomas Orlando, a professor at Georgia Tech’s School of Chemistry and Biochemistry.
These protons penetrate just 10 nanometers (four ten-millionths of an inch) below Mercury's surface. After colliding with hydroxyls, these molecules migrate to the surface, where heat can transform them into vapor, allowing for transport to the polar craters.
One lingering question is how asteroids that impacted Mercury acquired their water in the first place. Researchers propose that the processes outlined in this new study could explain the water on asteroids that occasionally collide with both Mercury and the Moon. Even in the absence of water, asteroid impacts might generate water, scientists suggest.
As humanity ventures further into the Solar System, access to water will be crucial for drinking and fuel. While a human mission to Mercury is unlikely in the near future, this research indicates that water may be located in the most unexpected places.
James Maynard is the founder and publisher of The Cosmic Companion. A New England native, he now resides in the desert of Tucson with his wife Nicole and their cat Max.
Did you enjoy this article? Join us on The Cosmic Companion Network for our podcast, weekly video series, informative newsletter, news updates on Amazon Alexa, and more!